Monday, June 27, 2016
Friday, June 24, 2016
Brexit - Everything Good? Not Really. You Better Get Ready for More EU Exits.
Cartoons from Hedgeye on Brexit:
More referendum likely to follow in France, Netherlands, Italy, Norway, etc. Is this the beginning of the end of the European Union / Euro? Immigration and globalization/trade will be the political issues for the remainder of 2016 in US and Europe.
Tuesday, June 14, 2016
Falling, Negative Interest Rates Concern Jim Bianco, Leading Market Observer
Jim Bianco Comments on Falling (and Negative) Long-Term Interest Rates
Most readers of this blog know that James A. Bianco,
who is President of Bianco Research, is a former Marquette student of
mine. He is one of the leading financial market observers and since 1990 he has
been producing fixed income commentaries distributed to institutional portfolio
managers and traders.
His commentary today is especially important. Jim writes:
“In the seminal book A History Of Interest Rates, Sidney Homer and Richard Sylla traced interest rates back to the fertile crescent in Mesopotamia 5,000 years ago. Nowhere in the book will you find negative interest rates (last update was 2005).
The
chart above shows that today Germany became the third country to see negative
interest rates at the 10-year tenor. They join Switzerland, who’s rates went
negative in early 2015, and Japan, who’s rates went negative earlier this year.
So
human history has no experience with negative interest rates. No one knows how
financial markets and economies are supposed to react to them. Are lower rates,
even if negative, stimulative? Or when rates go negative do we enter an
alternative universe where relationships change? This is our bet. All we have
are guesses, most of which have not panned out. See the yen strengthening since
Japan went negative on January 29. This was not the outcome that was expected.
We
better start figuring out how negative rates impact traditional relationships
in markets fast. As the next chart shows, we are now up to $13 trillion of
negative sovereign yields.”
You can contact Bianco Research at: http://www.arborresearch.com/bianco/
Sunday, June 12, 2016
A Table of Fixed Income Performance by Sector Over the Past Decade
In preparation for the Fixed Income course (FINA 4065) at Marquette, I came across this useful historical information from Ziegler Capital Management on the historical returns of fixed income securities.
Not surprisingly, high yield bonds (the riskiest of the fixed income securities included in the analysis) had an average annual return of 6.81% during the ten year period ended in 2015. What I didn't expect was to see that Municipal bonds were the strongest 3- and 5-year performer (with munis in 2014 and 2015 being the top performer). REITs were the second strongest performer throughout the 3-, 5- and 10-year periods - these have equity and fixed-income like characteristics. Asset-backed securities were the weakest performers.
Periodic Table:
Fixed Income Sector Performance Analysis
(2006-2015)
Click on chart to access report
(Sector definitions below)
The chart provides a detailed look at Fixed Income performance over the past decade, broken down by 13 sectors. This visual presentation of the performance helps point out the dynamic nature of the space and some of the sector trends in performance that have developed over the past decade.
Highlights:
Learn more at www.zieglercap.com
Fixed Income Sector Descriptions
Asset-Backed Securities (ABS)- A security whose income payments and value are derived from and collateralized (or “backed”) by a specified pool of underlying assets. The pool of assets is typically a group of small and illiquid assets which are unable to be sold individually.
Agency - Debt issued by a federal agency or a government-sponsored enterprise (GSE) for financing purposes. These types of debentures are not backed by collateral, but by the integrity and credit worthiness of the issuer. Officially, agency debentures issued by a Federal Agency are backed by the full faith and credit of the United States government.
CMBS Commercial Mortgage-Backed Securities (CMBS) - A type of mortgage-backed security backed by commercial mortgages rather than residential real estate. CMBS tend to be more complex and volatile than residential mortgage-backed securities due to the unique nature of the underlying property assets.
Emerging Markets - International government bonds issued by emerging market countries that are considered sovereign (issued in something other than local currency) and that meet specific liquidity and structural requirements.
Global Credit - A global bond may be issued in the domestic currency, but the same issue may be offered in several countries at the same time. Global bonds may be traded either in domestic or foreign markets.
High Yield - A high-yield corporate or credit bond is a high-income paying bond with a below investment grade rating. Because of the higher risk of default, these bonds pay a higher yield than investment grade bonds.
Investment Grade - Bonds issued by corporations which are rated BBB- or higher by Standard & Poor’s or Baa3 by Moody’s. These corporate bonds have a relatively low risk of default.
Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS) - A bond secured by a residential mortgage or collection of these mortgages. These bonds can be issued by either GNMA, Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac and have maturities of either15, 20 or 30 years
Muniipal Bonds (Muni)- A municipal bond is a debt security issued by a state, municipality or county to finance its capital expenditures. Municipal bonds are exempt from federal taxes and from most state and local taxes, especially if the holder resides in the state of issue.
Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT)- A REIT is a type of security that invests in real estate through property or mortgages. They receive special tax considerations and typically offer high dividend yields.
Term Loans - A term loan is a loan to a corporation which generally has a floating interest rate, is senior in the capital structure and is secured by a pledge of assets as collateral in the event of default.
Treasury Inflation Protected Securities (TIPS) - A treasury security that is indexed to inflation in order to protect investors from the negative effects of inflation. TIPS are considered an extremely low-risk investment since they are backed by the U.S. government and since their par value rises with inflation, as measured by the Consumer Price Index, while their interest rate remains fixed.
Treasury - A treasury instrument is a marketable, fixed-interest U.S. government debt obligation. Treasury securities make interest semi-annually and the income that holders receive is only taxed at the federal level.
| ||||||
Thursday, June 9, 2016
Monthly Performance of the AIM Class of 2017's Student Managed Equity Funds
AIM Small Cap and International Funds are both up since the Class of 2017 began managing the portfolios on April 1, 2016
 The students in the Applied Investment Management (AIM) program at Marquette University are responsible for managing two equity portfolios with a market value in excess of $2 million.
The students in the Applied Investment Management (AIM) program at Marquette University are responsible for managing two equity portfolios with a market value in excess of $2 million. According to AIM Director, Dr. David Krause, “The student-managed AIM funds provide valuable, real-time applied learning in investment analysis and portfolio management. The AIM students gain real world experience related to the topics and theories that are presented in the curriculum. These student-managed funds serve as a capstone to the finance and accounting courses the students take during their junior and senior years at Marquette. It is truly one of the best forms of applied learning I’ve seen.”

How has the newest group of AIM students (the Class of 2017) performed thus far? Below you will see a table that shows the first two months of performance for the AIM Small Cap and AIM International Equity portfolios.
The answer is that they've done fine. The two funds are both holding their own thus far - and both are up, but slightly below their respective benchmarks as of the end of May.
The Class of 2017 has added about 20 stocks to the two funds since April 1st, so they will need some time for their various investment ideas to play out. We'll continue to provide regular updates regarding the Class of 2017's equity performance.
(Click on the tables to enlarge)
Wednesday, June 8, 2016
Marquette University AIM Student, Leo Martinic, Recently had a Paper Published on Zerohedge
And so I introduced the students to Zerohedge as part of the curriculum. At the beginning of the course I reached out to Zerohedge with an idea. I had planned that the final exam would take the form of a take home project whereby each student would be tasked with some analytical problem. My proposal to Zerohedge was to publish the best final report. Zerohedge responded with an immediate “Absolutely”.
 |
| Leo Martinic presenting in AIM Room |
The second half of the course was spent applying the concepts of analysis to real world data. In effect, the concept of applied financial modeling is not DCF or any other specific formulaic model but the application of data in a useful and meaningful way toward some objective. This requires a deep understanding of the inter-relatedness of all stimuli within the context of risk, growth and cash flow.
 |
| Leo Martinic, AIM student |
The winning final
report was done by Leo Martinic, a junior and not surprisingly Leo is a member
of the AIM program, a student run investment group led by Business Faculty,
David Krause. This group manages about
$2M of the school’s endowment fund.
The assignment was
one question: Which is the better buy –
Amazon or Walmart?
Below is the
analysis presented by Leo Martinic.
FINA 4360 Leo Martinic Final Paper
Overview
A Look into Amazon
Amazon’s revenues have
soared since its inception, generating YoY growth of 20.2%, 19.5%, and 21.9%
for 2015, 2014, and 2013. Estimates for 2016 are even better, sitting at 24.7%.
This staggering revenue growth is due to CEO Jeff Bezo’s dedication to massive
capital expenditures and a current no dividend policy, averaging about $4.7
billion spent on capital expenditures per year over the past three fiscal
years. The capital expenditures have increased operating margins 943% in 2015
and 761% over the LTM. Although the huge plowback of cash into the business has
generated corresponding growth, it does not come without potential risk. It is
no guarantee that the large capital expenditures heading into the future will
yield Amazon’s historical growth rate. The ever-present risk with such large
capital expenditures is the fact that if it does not pay off by generating top
line results or cost efficiencies, then it is effectively flushing money down
the drain that could have otherwise been paid back to investors. This is
something Amazon and investors need to consider.
The organic growth is great, but operating expenses have grown 27.1%, 33.5%, and 35.8% for 2015, 2014, and 2013 along with similar, but not as severe, increases in COGS. The brunt of these hikes in cost are due to the increasing cost of shipping. In fact, the firm has been losing money on the shipping aspect of “Amazon Prime”. In 2015, Amazon charged $6.5 billion for shipping and ended up spending $11.5 billion, resulting in a shortfall of $5 billion. The shipping cost issue needs addressing if margins are going to improve. An issue with Amazon’s huge growth is that it has only yielded break-even bottom line results. It seems as if investors are infatuated with the staggering growth, but are not worried about current profit generation given Amazon is trading at a current P/E of 295.93 and the firm’s P/E has reached as high as 537 over the past year.
Management has continually
stated their current focus is on free cash flow, which they expect to generate
a significant bottom line result when the growth phase scales back. The belief
is that the massive capital expenditures will have set a foundation for
revenues to continue their climb while the focus shifts toward cost efficiency.
The promise of cash flow finally came to fruition in 2015, as Amazon generated
$7.33 billion in free cash flow yielding a 276% increase over the prior year.
Analysts believe this is the turning point for Amazon and expect these
staggering numbers to continue, starting with the top line and filtering to the
bottom line.
One worrisome fact with
Amazon is that total debt has also increased at a similar rate as just about
every one of the firm’s glowing statistics, increasing at a 58.6% CAGR over the
past five years. With Amazon we have massive revenue growth, high debt and
expenses, slim to no margins (other than gross margin!), and no true profit (as
of yet). As I was sifting through Amazon’s SEC filings, I found an 8-K worth
noting from February.
Amazon’s board of directors authorized a $5 billion share buyback plan, which I believe indicates that management is weary about earnings growth and will resort to considerable buybacks to inflate the stock price heading into the future. The buyback could be a signal that the growth story is nearing its end and this authorization could be a back-pocket option to hold up the stock price along with distributing cash with which the firm cannot find another productive use. The counter argument is that if substantial negative interest rates permeate over to the U.S., then Amazon would rather hold their own stock than lose money by sitting on idle cash.
Amazon’s board of directors authorized a $5 billion share buyback plan, which I believe indicates that management is weary about earnings growth and will resort to considerable buybacks to inflate the stock price heading into the future. The buyback could be a signal that the growth story is nearing its end and this authorization could be a back-pocket option to hold up the stock price along with distributing cash with which the firm cannot find another productive use. The counter argument is that if substantial negative interest rates permeate over to the U.S., then Amazon would rather hold their own stock than lose money by sitting on idle cash.
A Look into Walmart
Walmart is a completely
different story. Walmart’s revenue growth has slowly deteriorated from 11.8% in
2007 to -0.7% in 2016. This deterioration is signalling the world is moving
away from the “brick-and-mortar” provided by Walmart and more towards the
currently preferable online shopping. And perhaps more alarming the growth
deterioration may be signalling that consumption could actually be in decline..
With the decrease in revenue growth, Walmart has seen its operating income,
pretax income, and net income decrease 12.6%, 14.2%, and 10.2% respectively
from 2015 to 2016. This is the first time Walmart has seen such a pullback in
their historically superb results. Walmart’s workforce also received a
substantial wage hike of around $1.5 billion, which is bound to increase
notably in the future.
Walmart’s P/E sits at
14.71, not far off from its five-year average of 14.83. It is obvious that
Amazon and its online-only platform has eaten into Walmart’s grip on the retail
sector. With the fall in performance, Walmart continues to pay a 2.95% dividend
yield amounting to a $6.3 billion payout for 2016. The firm only carries $8.7
billion in cash on its balance sheet, so as cash flows begin to descend
Walmart’s ability to fund a high dividend payout will be questionable at best.
Cash dividend coverage has decreased from 6.39 in 1999 to 2.33 today, including
an alarming 10.3% drop from 2015 to 2016 alone. Walmart will continue to run
into trouble generating the cash necessary to pay their high dividend and soon
enough the firm will have to borrow in order to continue to satisfy shareholders.
With no growth, Walmart
will have to adjust in order to combat Amazon for the crown of the retail
sector. Walmart is the perfect case of how investors are looking for immediate
gratification, whether through stock price appreciation or through dividends.
Such a strategy ignores the fact that Walmart is being forced to cannibalize
itself from the inside out by trading future growth to satisfy investor hunger
today. In addition, Walmart has slowly bought back shares since the turn of the
century. In 2000, Walmart had 4.4 billion shares outstanding in contrast to the
3.1 billion outstanding today. The firm has decreased its outstanding shares
about 1-4% every year, while repurchasing 7.1% in 2011 alone. I view this as
management’s attempt to artificially prop up the stock price along with
maintaining ratios as results have plateaued and begin their inauspicious
descent. It also takes significant cash to maintain these repurchases again a
form of economic cannibalization..
Up to this point I seem to
be forecasting a disastrous spiral into irrelevance for Walmart, but let me be
clear that the firm is not going away any time soon. Walmart has about 4.8x the
annual revenue of Amazon and the firm’s accessibility around the world is
unmatched. Also of similar importance, Walmart is a good risk averse investment
for those who depend on large dividends from blue chip companies as annual
income. However it is my opinion that these very things that make Walmart a
risk averse asset in the short term could spell trouble further out; decreasing
cash flows, waning profitability, breached competitive advantage, a high
dividend payout to appease shareholders, and the continuous eating of shares to
prop up the stock price all portray Walmart’s imminent cash problem for the
future.
Conclusion
Overall, I think the better
buy is Amazon, but not for the reasons you might think. Personally, I do not
believe Amazon’s future lies with their online retail, but rather the firm’s
AWS (Amazon Web Services) subsidiary. With strong growth prospects for their
AWS segment, my DCF came to a price target of $924.34 per share for Amazon.
Amazon is an incredible growth story with endless potential in a world where
people demand to get products quickly without any real effort, but the firm’s
core online retail business has not made money.
The business idea is
terrific, but in order for Amazon to make money they need to raise the annual
“Amazon Prime” fee well above $99. The issue is that price increases will steer
customers away, so Amazon needs to make a choice. Should they continue their
low priced “Amazon Prime” to increase their customer base and revenues while
making no profit? Or should they increase prices, which will drive away some
customers but will result in profit generation?
The question is whether Bezos can slash costs, most notably shipping
costs, while maintaining a high quality and expedited shipping process.
As of now, that seems more
like a pipe dream than a reality.
However, this past week, Amazon entered into a partnership with Atlas
Air in order to add twenty Boeing airplanes to its operations, so it is not for
a lack of trying. Amazon’s core business reminds me of the tech bubble of
1999-2000. Amazon’s P/E of 295.93 is nothing short of crazy and already prices
in projected best case success for the firm. The reality is that Amazon has
been operating for 22 years and their core business still cannot generate a
profit. The core business’ inability to generate a profit will catch up with
the firm and its stock price unless they adapt. The laws of finance can be
bent, but they will not break. Fortunately for Amazon I believe the fundamental
growth prospects from high investment has and will continue to produce ground
breaking innovation resulting in realized growth.
If Amazon is going to
generate a substantial profit, it will be realized through their promising AWS
subsidiary. This may sound contradictory, as I said Amazon reminds me of the
tech bubble, but here I am championing their “tech” segment.
Source: Techcrunch
However, the situation is
quite different. Amazon’s AWS segment has posted increasing profits and is well
ahead of the competition in the cloud computing industry. From Amazon’s
website, “Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a secure cloud services platform,
offering compute power, database storage, content delivery and other
functionality to help businesses scale and grow”. The segment is posting a
bigger operating income than Amazon’s core business.
Source: Seekingalpha.com
AWS accounts for about 8%
of the firm’s revenue but over half of their profitability in the first quarter
of 2016. Businesses are buying into AWS faster than any other cloud-computing
firm in the industry. Netflix delivers its streaming capabilities through AWS;
Healthcare.gov runs partly through the service, and music giant Spotify is
built on the service as well, just to name a few. Amazon even engineered a
custom cloud for the CIA and other intelligence agencies in order to share
information. It is apparent that AWS has quietly become a vastly important
service.
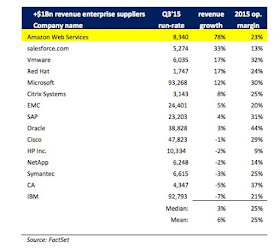
In this table we see that
Amazon’s AWS is witnessing the best of both worlds that it cannot quite find
within its core business, which is tremendous growth in revenues along with
profit generation. The operating margin is in line with the industry while
swiftly increasing market share at an unmatched pace. Overall, I believe AWS is
the future for Amazon. All businesses need cloud computing to operate in the
21st century. Businesses contemplating making the switch seem to flock to AWS
in droves. Deutsche Bank recently stated that if AWS were a standalone
business, it could easily be valued at around $160 billion.
Walmart had its success in
the past, but the decrease in revenues and overall financial performance in
2016 foreshadow what will be a slow descent from atop the retail pedestal. My
DCF resulted in a price target of $65.03 for Walmart. With tremendous growth
and profitability in AWS, Amazon essentially buys itself time to figure out how
to iron out their core online retail business to generate profitability. If
Amazon does continue its burst onto the retail scene and finally improve
margins, Walmart will have to adjust its strategies or cash flows will erode
while the firm continues to spend huge amounts of cash on dividends and share
buybacks, effectively leading the firm into self-cannibalism.
So if I had $700 sitting around, I would much rather have one share of Amazon than ten shares of Walmart!
So if I had $700 sitting around, I would much rather have one share of Amazon than ten shares of Walmart!